Gaza Ceasefire Deal:
A New Dawn for Peace
A comprehensive analysis of the historic ceasefire agreement, key players, and future implications for Middle East peace
The Ceasefire Agreement: Key Terms
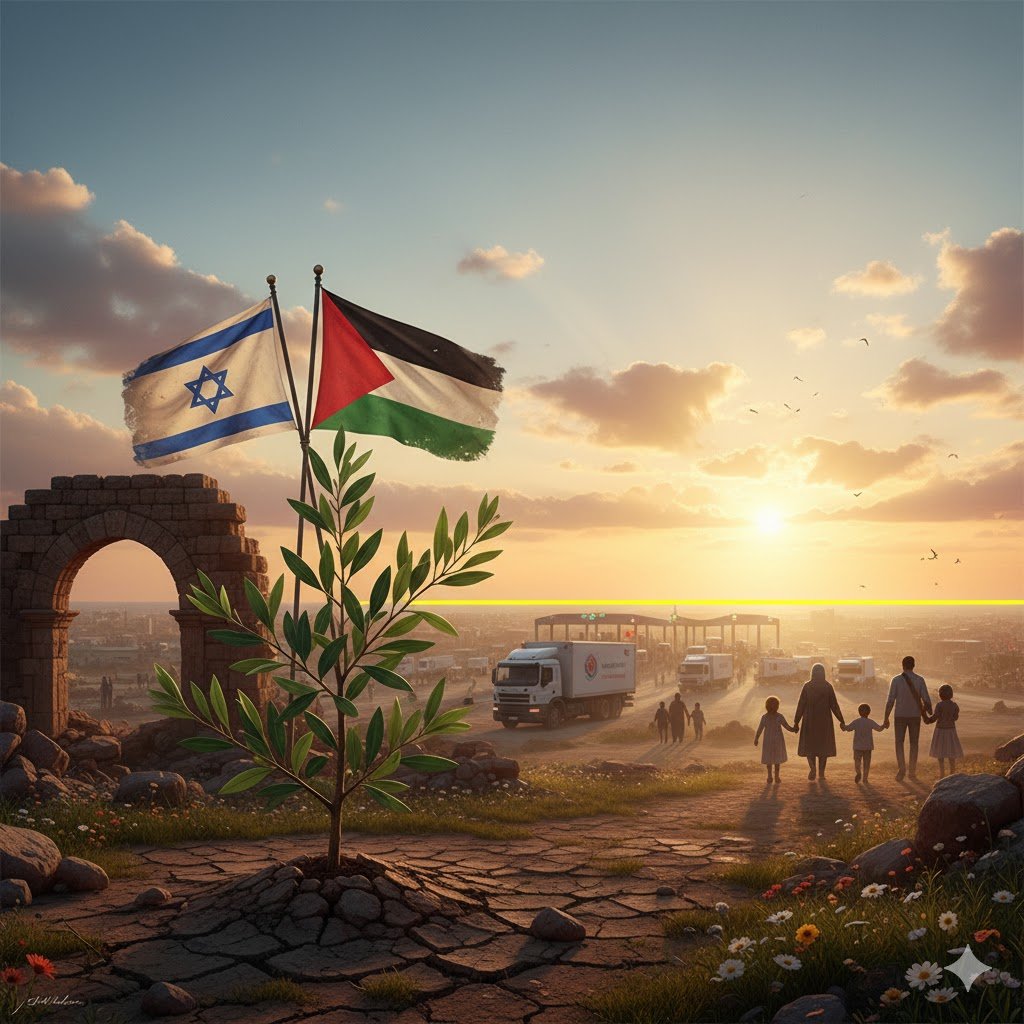
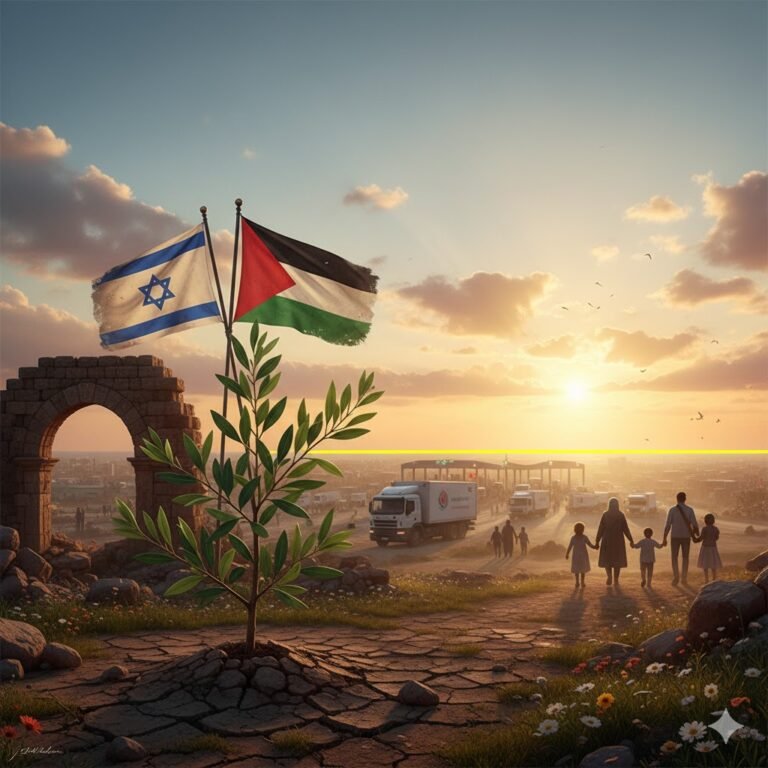
The Gaza ceasefire officially commenced on October 10, 2025, at 12:00 PM local time after Israel’s cabinet approved the agreement in the early hours of Friday morning. This represents the first phase of what has been termed Trump’s 20-point peace plan, announced on September 29, 2025.
Immediate Terms of Phase One
Hostage and Prisoner Exchange
Hamas will release all 20 surviving Israeli hostages within 72 hours of Israel’s troop withdrawal. Israel will release approximately 250 Palestinian prisoners serving life sentences and 1,700 detainees from Gaza.
Military Withdrawal
Israeli forces have completed their initial withdrawal to the “yellow line,” maintaining control over approximately 53% of the Gaza Strip.
Humanitarian Aid
A minimum of 400 aid trucks will enter Gaza daily, with numbers expected to increase gradually to 600 trucks daily.
Trump’s Central Role
President Donald Trump emerged as the primary architect of this ceasefire agreement, leveraging both diplomatic pressure and strategic relationships across the Middle East. Trump’s approach combined his administration’s strong support for Israel with threats of consequences if Hamas rejected the deal.
Key Negotiators
Steve Witkoff
Trump’s special envoy and fellow real estate developer
Jared Kushner
Leveraged Middle East experience from Trump’s first term
“Trump’s deadline-driven approach proved effective, giving Hamas until October 5, 2025, to accept his proposal, warning of ‘all hell’ if they refused.”
International Mediation
The ceasefire agreement represents a triumph of Arab diplomatic mediation, with Qatar, Egypt, and Turkey playing indispensable roles. These nations served not only as intermediaries but as guarantors of the agreement’s implementation.
Qatar’s Role
As a key mediator throughout the conflict, Qatar maintained relationships with both Hamas leadership and international partners. The nation’s diplomatic infrastructure proved crucial in facilitating communication between parties that do not directly negotiate.
Egypt’s Strategic Position
Egypt’s control of the Rafah border crossing and its historical role in Gaza ceasefire negotiations made it an essential partner. Egyptian President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi worked closely with Trump’s team to finalize the agreement.
Turkey’s Influence
President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s recent discussions with Trump, during which Trump specifically requested Turkish assistance in convincing Hamas to accept the plan, proved pivotal in the final breakthrough.
US Military Involvement: Monitoring and Enforcement
Deployment of American Forces
The United States has deployed approximately 200 military personnel to Israel to monitor ceasefire implementation. These troops, stationed at Hatzor Air Base in southern Israel, will operate as part of a multinational task force under US Central Command leadership.
📍 Mission Scope
The American contingent will establish a Joint Control Center to coordinate with multinational forces from Egypt, Qatar, Turkey, and the UAE. No US troops will enter Gaza itself.
⚡ Operational Framework
Led by Admiral Bradley Cooper, head of US Central Command, including specialists in logistics, transportation, security, and engineering.
The Human Cost: Understanding the Devastation
Casualty Statistics and Impact
The two-year Gaza war has resulted in unprecedented casualties and destruction:
Palestinian Casualties
Israeli Casualties
Infrastructure Destruction
Over 90% of Gaza’s homes have been damaged or destroyed, leaving nearly 1.9 million Palestinians displaced. The territory’s healthcare system has completely collapsed.
Humanitarian Crisis Dimensions
Famine Conditions
461 malnutrition deaths, 1.9M facing food insecurity
Healthcare Collapse
No functioning hospitals remaining
Aid Worker Deaths
565 aid workers killed, including 179 UNRWA staff
Legal and International Implications
War Crimes Allegations
International legal bodies and human rights organizations have documented extensive evidence of war crimes by both parties:
UN Findings
The UN Human Rights Council has identified “clear evidence” of war crimes by both Hamas and Israeli forces. A detailed UN analysis found that 70% of Palestinians killed in residential areas were women and children.
International Criminal Court
The ICC has issued arrest warrants for leaders on both sides, including Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Hamas officials, alleging criminal responsibility for war crimes and crimes against humanity.
Genocide Allegations
South Africa’s case at the International Court of Justice accuses Israel of genocide, with the ICJ ruling it “plausible” that Israel is breaching the Genocide Convention. Multiple international legal experts and human rights organizations have made similar determinations.
Trump’s 20-Point Peace Plan: Future Phases
Comprehensive Framework for Peace
Trump’s plan extends far beyond the current ceasefire, outlining a three-phase process for ending the conflict and reshaping Gaza’s future:
2 Phase Two Objectives
- • Establishment of permanent ceasefire with “sustainable calm”
- • Complete Israeli withdrawal from Gaza
- • Release of remaining Israeli hostages
- • Implementation of transitional governance structures
3 Phase Three Vision
- • Exchange of remains of deceased hostages
- • Opening of border crossings
- • Beginning of comprehensive reconstruction program
- • Establishment of deradicalized, terror-free governance
Governance Transition Plans
The plan envisions Gaza’s transformation under international supervision:
Transitional Authority
A “technocratic, apolitical Palestinian committee” would assume day-to-day governance under an international board headed by Trump and former British Prime Minister Tony Blair.
Hamas Exclusion
The plan explicitly excludes Hamas from any future governance role, requiring the organization to disarm completely. Recent statements from Hamas sources indicate the group may be prepared to relinquish control, though disarmament remains contentious.
Palestinian Authority Role
Despite being sidelined in initial plans, Palestinian Authority officials express confidence they will play a significant role in Gaza’s future governance, citing Arab state support and their existing presence in the territory.
Critical Challenges and Future Prospects
Immediate Implementation Risks
Several factors could jeopardize the ceasefire’s sustainability:
Historical Precedent
The last ceasefire between Israel and Hamas collapsed in March 2025 when negotiations for a second phase failed, leading to resumed hostilities. This pattern raises concerns about long-term viability.
Enforcement Mechanisms
The agreement’s success depends heavily on the effectiveness of international monitoring forces and the commitment of both parties to honor their obligations.
Gaza’s Devastation
The scale of destruction in Gaza presents enormous challenges for reconstruction and governance transition, potentially creating conditions for renewed instability.
Long-term Geopolitical Implications
The ceasefire agreement carries significant implications for regional stability:
Abraham Accords Expansion
Success could facilitate Israeli-Saudi normalization
Palestinian Statehood
Two-state solution implementation remains uncertain
Regional Dynamics
Could reshape diplomatic relationships and Iran’s influence
International Response and Support
Global Diplomatic Backing
The ceasefire has received widespread international support:
Arab World Response
Leaders across the Middle East have praised the agreement, with particular recognition for the mediation efforts of Qatar, Egypt, and Turkey.
European Support
European leaders have welcomed the deal while emphasizing the need for sustainable peace and Palestinian rights.
UN Position
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres commended the diplomatic breakthrough while calling for full compliance with international humanitarian law.
Conclusion: A Fragile but Historic Opportunity
The Gaza ceasefire represents the most significant diplomatic breakthrough in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict in recent years. Trump’s successful orchestration of this agreement, leveraging relationships with Arab partners and applying strategic pressure, has created an unprecedented opportunity for lasting peace.
The Path Forward
However, the agreement faces substantial challenges. The scale of destruction in Gaza, the complexity of governance transitions, and the historical pattern of failed ceasefires all present risks to long-term success. The critical test will come in the implementation of subsequent phases, particularly Hamas’s disarmament and the establishment of sustainable governance structures.
The involvement of US troops in monitoring roles, combined with Arab state commitments to mediation and reconstruction, provides a more robust framework than previous ceasefire attempts. Yet the ultimate success depends on both parties’ willingness to make the difficult compromises necessary for lasting peace.
A Moment of Hope
As Palestinians begin returning to devastated communities and families prepare for hostage releases, this moment represents both an end to immediate suffering and the beginning of an uncertain but potentially transformative chapter in Middle Eastern politics. The coming weeks and months will determine whether this ceasefire marks the foundation for enduring peace or merely another temporary pause in a decades-long conflict.